WebAPI/WebTelephony: Difference between revisions
< WebAPI
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Status) |
(consolidate and update WebTelephony) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Goals == | == Goals == | ||
The aim of WebTelephony is to establish a DOM API, which allows web content to dial out and mediate | The aim of WebTelephony is to establish a DOM API, which allows web content to dial out and mediate calls, i.e. answer, reject, hold or resume a call. | ||
== Status == | == Status == | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
WebTelephony meta bug: {{bug|674726}} | WebTelephony meta bug: {{bug|674726}} | ||
B2G meta | B2G telephony meta bug: {{bug|699235}} | ||
== Implementation Specifics == | == Implementation Specifics == | ||
=== | === Telephony call states === | ||
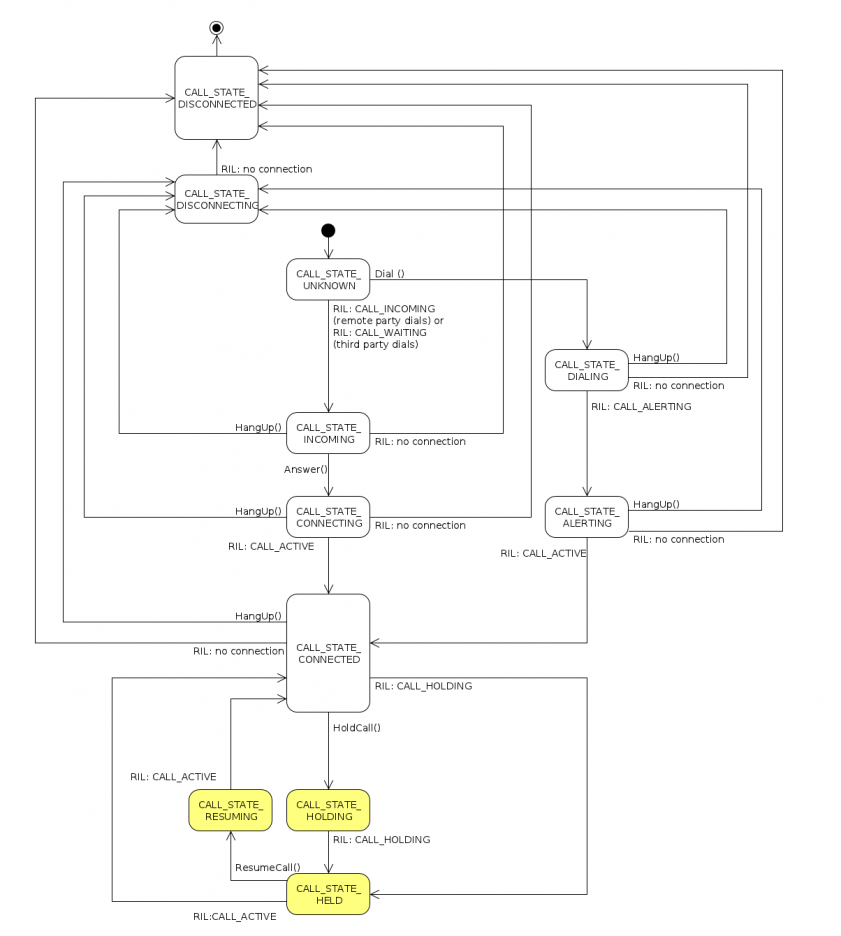
The diagram below shows the current design of B2G telephony call states. | |||
The diagram below shows the current design of B2G telephony call states | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 27: | Line 25: | ||
[[Image:Proposal TelephonyCallStates v2.png|842x936px|Proposal of telephony call states to support call holding]]<br> | [[Image:Proposal TelephonyCallStates v2.png|842x936px|Proposal of telephony call states to support call holding]]<br> | ||
=== | === DOM API === | ||
interface nsIDOMTelephony: nsIDOMEventTarget | |||
{ | { | ||
nsIDOMTelephonyCall dial(in DOMString number); | nsIDOMTelephonyCall dial(in DOMString number); | ||
| Line 47: | Line 45: | ||
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onincoming; | attribute nsIDOMEventListener onincoming; | ||
attribute nsIDOMEventListener oncallschanged; | |||
}; | }; | ||
| Line 60: | Line 52: | ||
readonly attribute DOMString number; | readonly attribute DOMString number; | ||
// "dialing", "alerting", "busy", "connecting", "connected", "disconnecting", "disconnected", "incoming" | // "dialing", "alerting", "busy", "connecting", "connected", "disconnecting", "disconnected", "incoming", "holding", "held", "resuming" | ||
readonly attribute DOMString state; | readonly attribute DOMString state; | ||
| Line 74: | Line 65: | ||
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onstatechange; | attribute nsIDOMEventListener onstatechange; | ||
attribute nsIDOMEventListener ondialing; | |||
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onalerting; | attribute nsIDOMEventListener onalerting; | ||
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onbusy; | attribute nsIDOMEventListener onbusy; | ||
| Line 82: | Line 72: | ||
attribute nsIDOMEventListener ondisconnecting; | attribute nsIDOMEventListener ondisconnecting; | ||
attribute nsIDOMEventListener ondisconnected; | attribute nsIDOMEventListener ondisconnected; | ||
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onincoming; | |||
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onholding; | attribute nsIDOMEventListener onholding; | ||
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onheld; | attribute nsIDOMEventListener onheld; | ||
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onresuming; | attribute nsIDOMEventListener onresuming; | ||
}; | }; | ||
Revision as of 06:26, 6 June 2012
Goals
The aim of WebTelephony is to establish a DOM API, which allows web content to dial out and mediate calls, i.e. answer, reject, hold or resume a call.
Status
WebTelephony meta bug: bug 674726
B2G telephony meta bug: bug 699235
Implementation Specifics
Telephony call states
The diagram below shows the current design of B2G telephony call states.
State transition in detail:
- Scenario #1: There is no other call on-line (current design)
When a remote party dials, a new call is generated with its call index (no. 1), and the call state now is CALL_STATE_INCOMING.
When user answers/hangs up the call, the call state is eventually pushed to CALL_STATE_CONNECTED/CALL_STATE_DISCONNECTED according to user's decision. - Scenario #2: There is already a call on-line
When the third party dials, a new call is generated with the state of CALL_STATE_INCOMING. Since there is already a call on-line, the new call's index is no. 2.
When user answers the new call (call no. 2), its state is going to be transferred to CALL_STATE_CONNECTED.
In the meanwhile, the state of the originally connected call (call no. 1) should be forced to CALL_STATE_HELD. - Scenario #3: User wants to hold a call when there's no waiting call
User can |HoldCall()| to change the call state from CALL_STATE_CONNECTED to CALL_STATE_HELD.
User can |ResumeCall()| to make a call from CALL_STATE_HELD back to CALL_STATE_CONNECTED.
DOM API
interface nsIDOMTelephony: nsIDOMEventTarget
{
nsIDOMTelephonyCall dial(in DOMString number);
attribute boolean muted;
attribute boolean speakerEnabled;
// The call that is "active", i.e. receives microphone input and tones
// generated via startTone.
readonly attribute jsval active;
// Array of all calls that are currently connected.
readonly attribute jsval calls;
void startTone(in DOMString tone);
void stopTone();
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onincoming;
attribute nsIDOMEventListener oncallschanged;
};
interface nsIDOMTelephonyCall: nsIDOMEventTarget
{
readonly attribute DOMString number;
// "dialing", "alerting", "busy", "connecting", "connected", "disconnecting", "disconnected", "incoming", "holding", "held", "resuming"
readonly attribute DOMString state;
void answer();
void hangUp();
//make a "connected" call into "held"
void hold();
//make a "held" call back to "connected"
void resume();
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onstatechange;
attribute nsIDOMEventListener ondialing;
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onalerting;
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onbusy;
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onconnecting;
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onconnected;
attribute nsIDOMEventListener ondisconnecting;
attribute nsIDOMEventListener ondisconnected;
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onincoming;
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onholding;
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onheld;
attribute nsIDOMEventListener onresuming;
};