Labs/F1/Modularity/WebMod HOWTO: Difference between revisions
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== Advertising a WebMod == | == Advertising a WebMod == | ||
A web site can advertise to user agents that it has WebMods available to answer certain API calls using | A web site can advertise to user agents that it has WebMods available to answer certain API calls using an Open Web App manifest: | ||
{ | { | ||
"version": "1.0", | "version": "1.0", | ||
"name": " | "name": "ShareBook", | ||
"description": " | "description": "Sharing with your Friends", | ||
"icons": { | "icons": { | ||
"16": "/img/icon-16.png", | "16": "/img/icon-16.png", | ||
"48": "/img/icon-48.png", | "48": "/img/icon-48.png", | ||
"128": "/img/icon-128.png" | "128": "/img/icon-128.png" | ||
}, | }, | ||
"developer": { | "developer": { | ||
"name": " | "name": "Share Inc.", | ||
"url": "http://shareacme.com" | |||
}, | }, | ||
"default_locale": "en" | "default_locale": "en" | ||
"experimental": { | |||
"services": { | |||
"link.share" : { | |||
"url": "/webmods/link-share", | |||
"name": "Share via ShareBook" | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | } | ||
== Implementing a WebMod == | == Implementing a WebMod == | ||
Revision as of 17:46, 15 June 2011
This HOWTO is specifically tailored to web sites that wish to be tightly integrated with Firefox functionality in the form of a Web Module (WebMod).
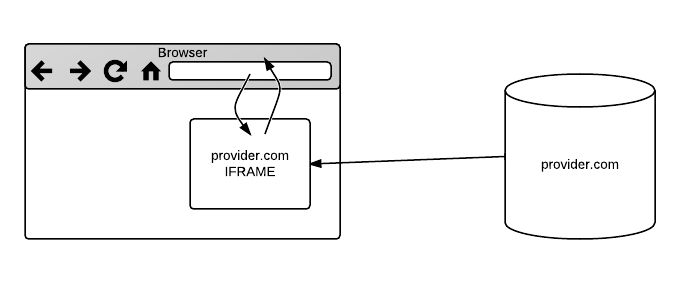
Architecture
A WebMod extends a well-targeted piece of browser functionality with HTML and JavaScript. WebMods have no standalone abilities to modify the user agent; they only respond to API calls from the user agent. A WebMod is made available by a provider, e.g. Twitter for link-sharing, as HTML and JavaScript served from the provider's domain. It is advertised by a Web-accessible manifest, and it can be "installed" into a user agent that supports this functionality.
The user agent and WebMods communicate over postMessage(). Effectively, a WebMod is a mechanism for a web site to expose an API to the user agent over postMessage().
Advertising a WebMod
A web site can advertise to user agents that it has WebMods available to answer certain API calls using an Open Web App manifest:
{
"version": "1.0",
"name": "ShareBook",
"description": "Sharing with your Friends",
"icons": {
"16": "/img/icon-16.png",
"48": "/img/icon-48.png",
"128": "/img/icon-128.png"
},
"developer": {
"name": "Share Inc.",
"url": "http://shareacme.com"
},
"default_locale": "en"
"experimental": {
"services": {
"link.share" : {
"url": "/webmods/link-share",
"name": "Share via ShareBook"
}
}
}
}