Gaia/Design/Patterns: Difference between revisions
| Line 301: | Line 301: | ||
*** Displays a looping animation, communicating to the user that the process is active. | *** Displays a looping animation, communicating to the user that the process is active. | ||
[[Image:Gaia_BB_Progress&Activity_1. | [[Image:Gaia_BB_Progress&Activity_1.png|Progress & Activity 1]] | ||
==Scrolling== | ==Scrolling== | ||
Revision as of 11:29, 11 June 2012
Design Patterns are core sets of interactions that are used repeatedly throughout the UX.
Design Specs
- Gaia_Patterns_20120525_V1.0.pdf (Josh Carpenter, May 25 2012)
- Version 1.0 of doc. Draft content, annotations needed, many sections not started.
Status & Team
Buttons
Characteristics:
- Have two components: visual target and hit target.
- Later is always larger. Has minimum sizes.
- Types:
- Icon + text
- Icon only
- Text only
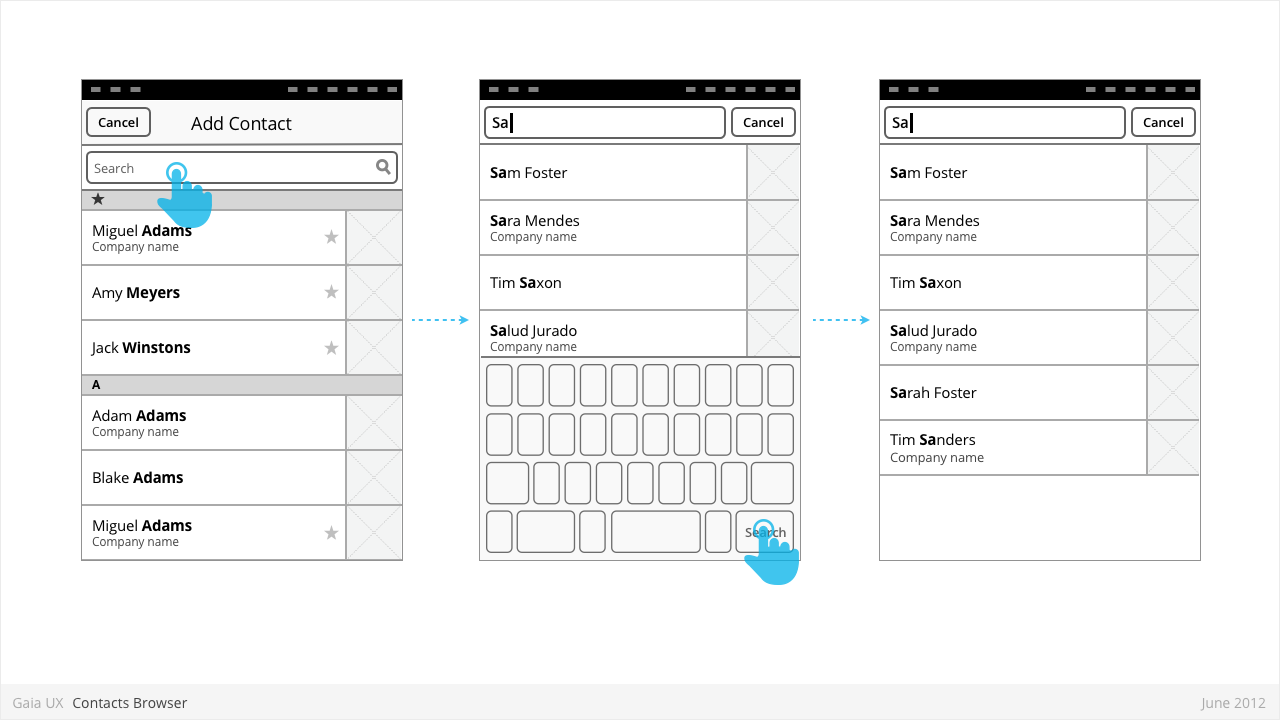
Contacts Browser
Used for:
- Adding a contact to a correspondence (eg: Email, SMS)
Characteristics:
- Is an example of an Entry Sheet dialogue.
- Opens when user selects “Add” button.
- Presents complete list of contacts.
- “Cancel” closes the Browser without making a select.
- Tapping a contact closes the Browser and adds the selected contact to the selected field.
- Uses index scrolling [ADD LINK]
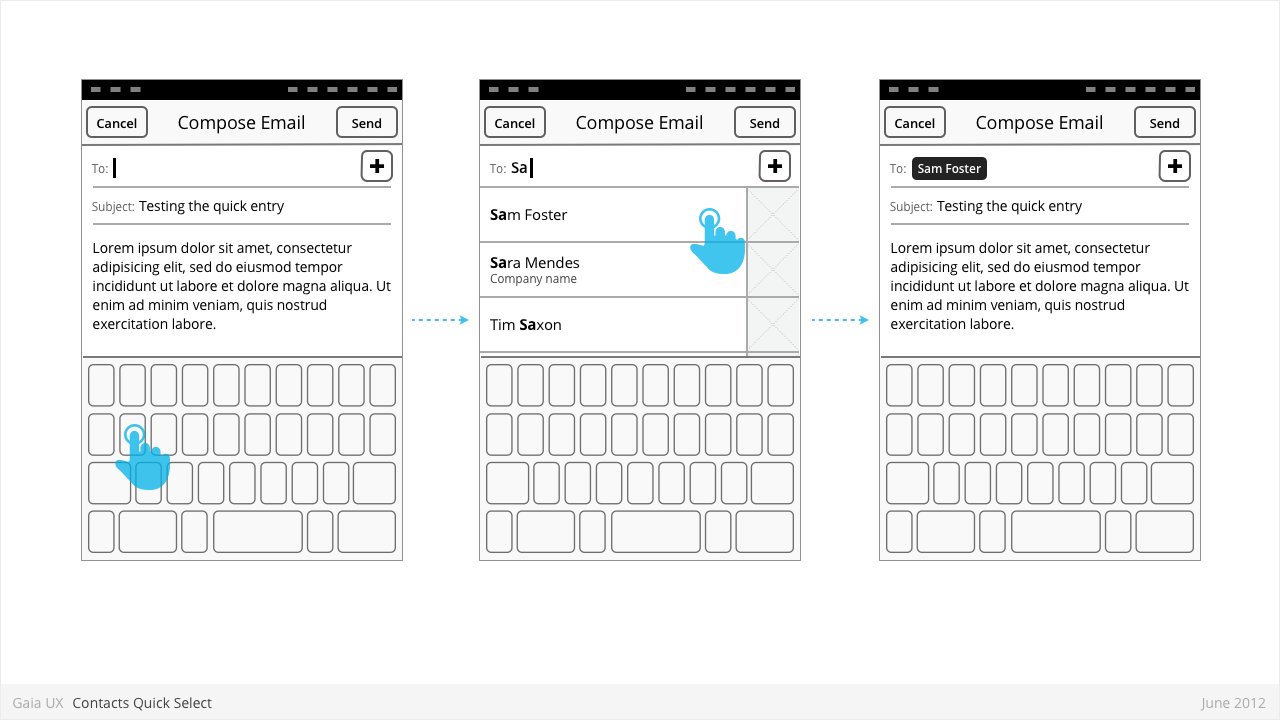
Contacts Quick Select
Used for:
- Selecting a known contact quickly, without leaving the current view.
Characteristics:
- The user highlights an entry field (eg: To), and the keyboard appears.
- As the user types, the system attempts to draw matches from the contacts.
- If one or matches are found, a small list appears, highlighting the matching contacts.
- To make a selection, the user can tap one of the rows, closing the list and adding that contact to the highlighted field.
- Alternatively, if the user wishes to clear the list, they can type Backspace until the field is clear, and there are therefore no more matches. The list then disappears.
Dialogues: Alerts
Used for:
- Alerting users to important events, notifications, etc.
Characteristics:
- Modal: occupies the screen and requires user input to clear.
- Consist of
- Title
- Body (optional)
- Dismissal button (eg: “Cancel”)
- Confirmation button (eg: “Delete”)
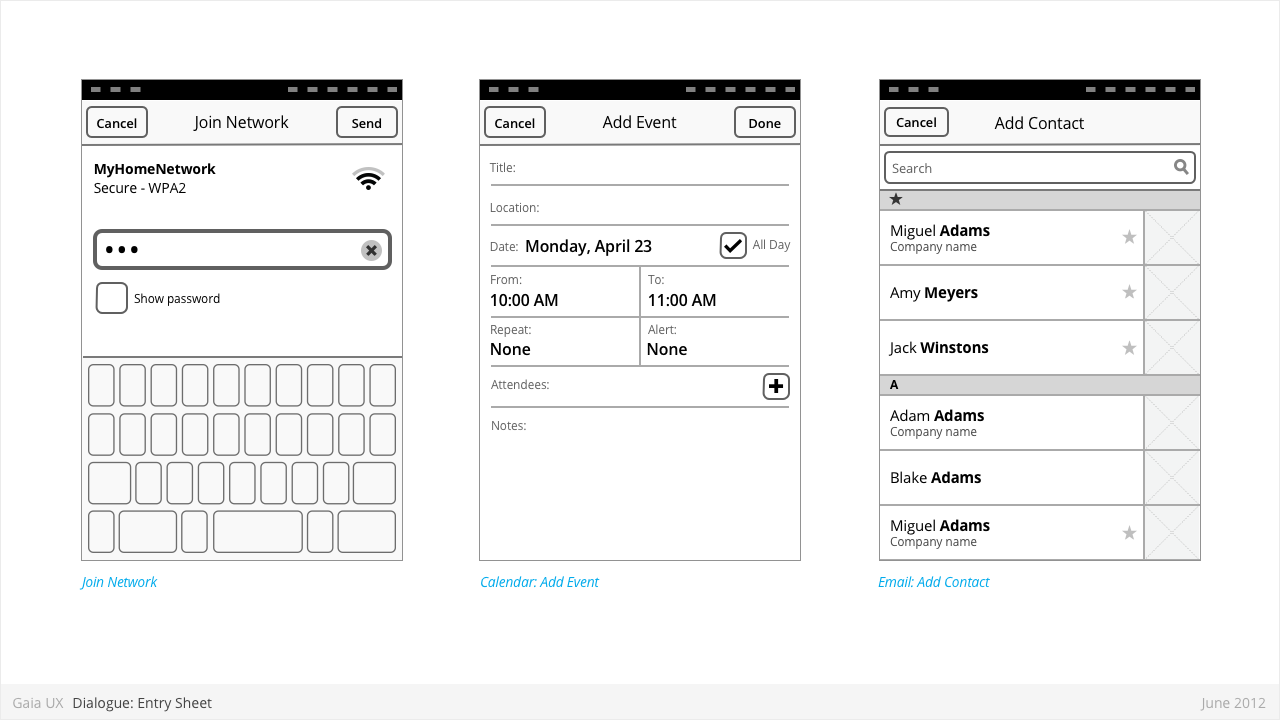
Dialogues: Entry Sheet
Used for:
- Editing a single setting that:
- Contains a large number of possible values. eg: Text entry forms, long lists,
- [or] Requires multipe inputs or selections eg: WiFi network connection process.
Characteristics:
- Occupies the full screen
- User should be given impression that they are on the same page, and that the Entry Sheet is merely a temporary modal overlay. They have not navigated one level deeper in the hierarchy.
- To reinforce this...
- Valid animations could include slide in from top, from bottom, cross fade, scale in, etc.
- “Cancel” buttons are used instead of “Back”.
- Every element within the Entry Sheet must be related to adjusting the single setting; Settings Panels should not contain links to other pages or lists.
- Closing:
- “Cancel”
- Varies: “Done”, “Join”, “Send”, etc.
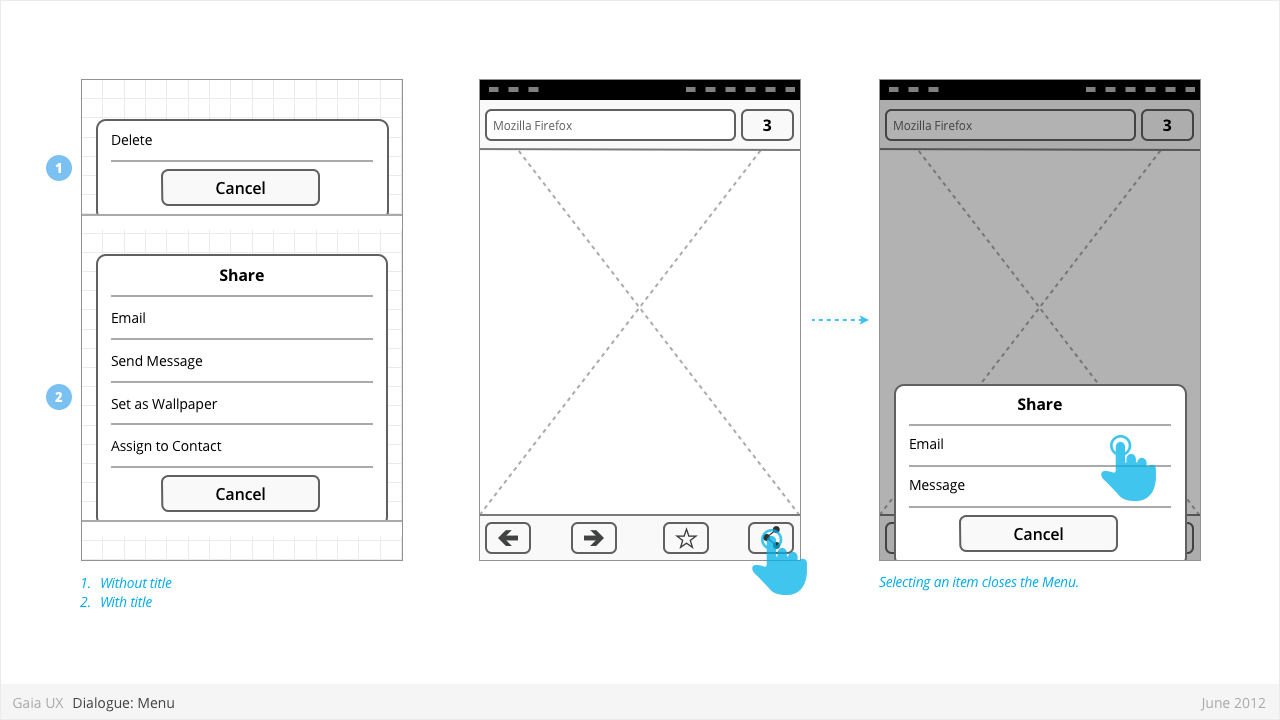
Dialogues: Menus
Used for:
- Selecting from one or more actions
- Inputing or selecting from a set of values (see: Value Selectors)
Characteristics:
- Menus are spawned from Toolbars or Forms selections.
- Vary in height, to a maximum of Keyboard component height.
- Present 1 or more items.
- Optional Title
- Close by:
- Selecting one of items
- Tap cancel button
- Tap “OK” button, if available (label name TBD)
- Value Selectors are examples of Menus, but not all Menus are Value Selectors.
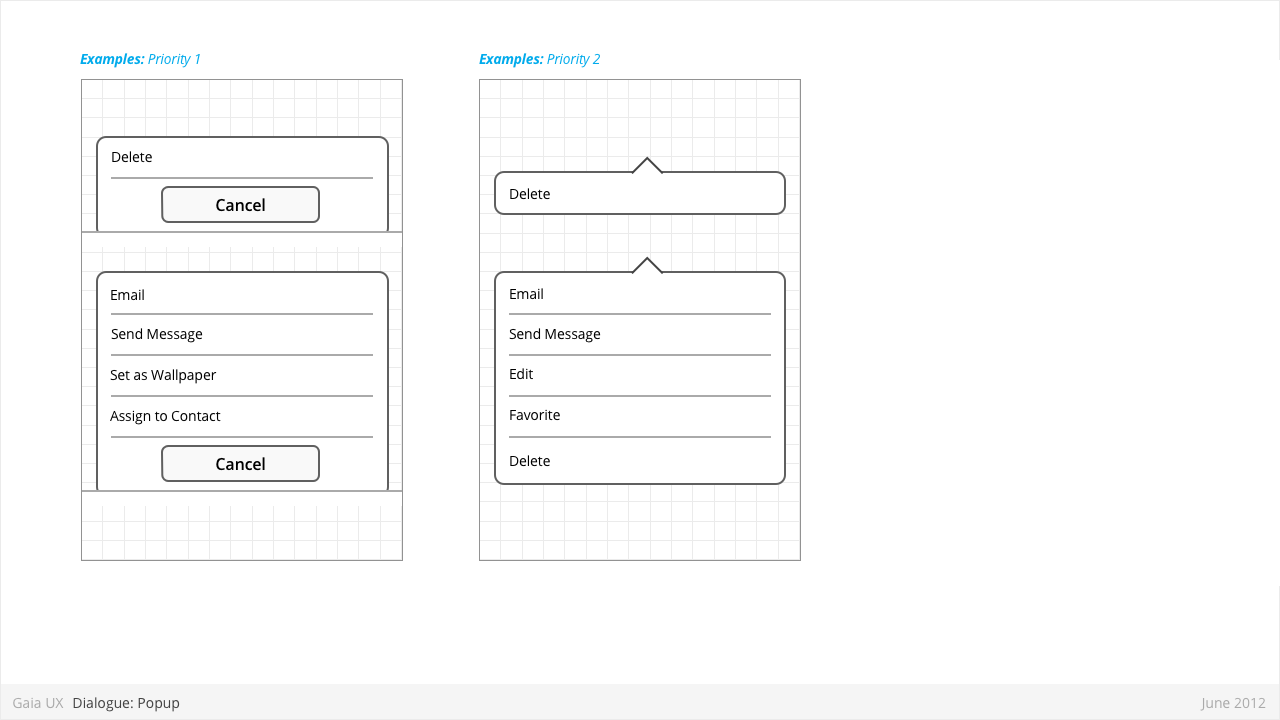
Dialogues: Popups
Used for:
- Enabling optional shortcuts to contextual actions that might otherwise require stepping one level deeper into the hierarchy. For example, deleting a photo via it's thumbnail, instead of having to open the full image.
Characteristics:
- User presses-and-holds a selectable item (can be a list row, a phone number, a browser link, etc)
- Menu displaying one of more options pops up after X seconds.
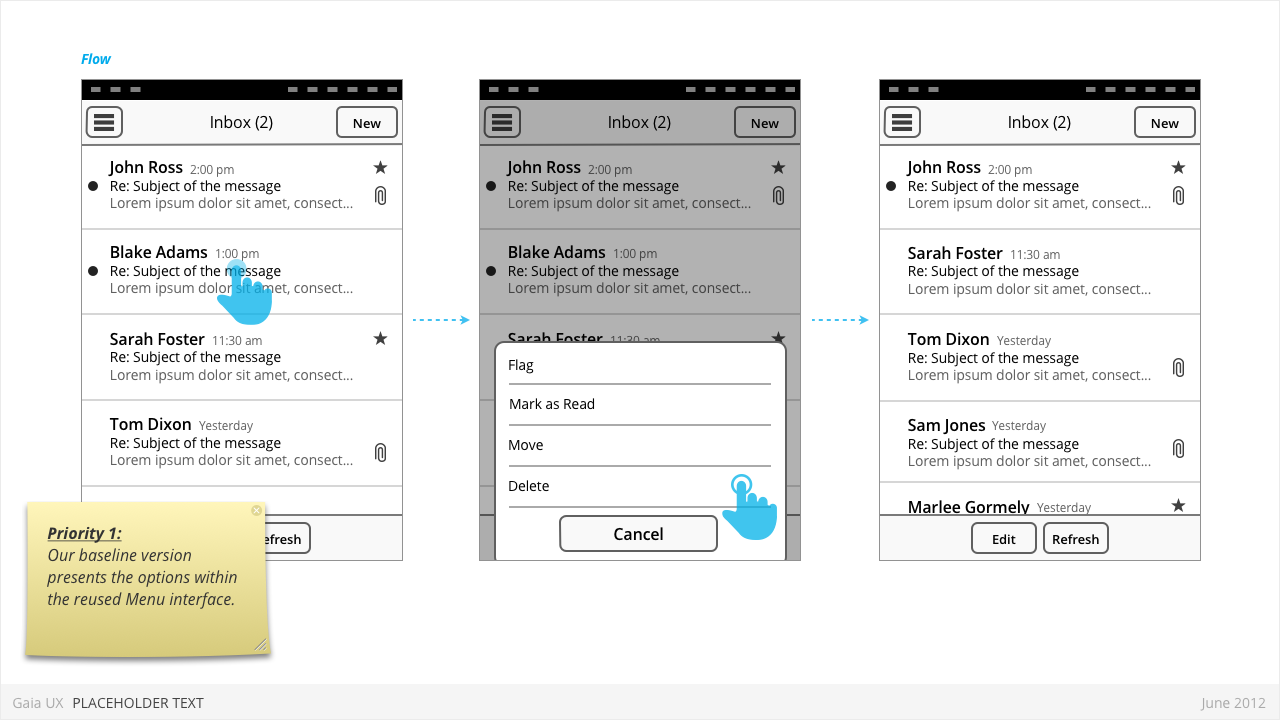
- Priority 1:
- Reused the Menu pattern interface to present the options.
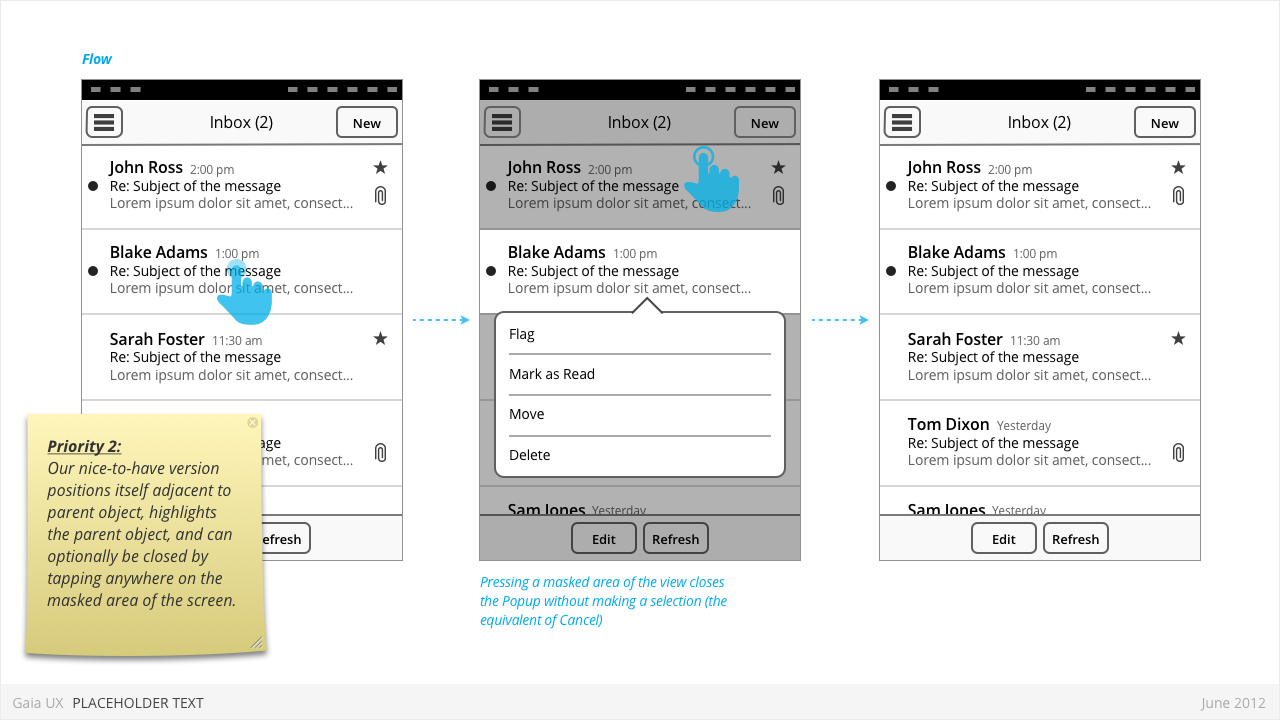
- Priority 2:
- Menu positions itself immediately above or below the parent object (depending on the amount of available screen space)
- The parent object element is visually highlighted (e.g.: darken surrounding content, or draw border, etc)
- User can press anywhere else on screen to change the focus and close the popup.
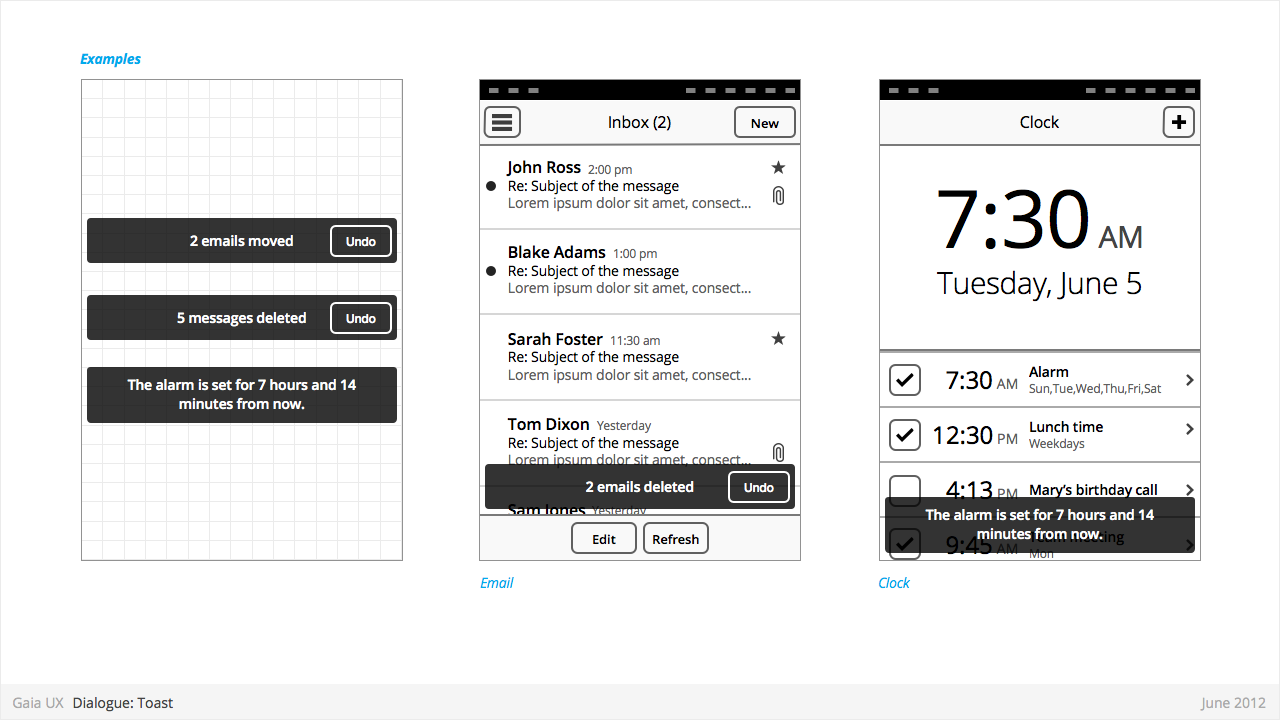
Dialogues: Toasts
Used for:
- Toasts confirm a user action, and optionally provide a follow up action (eg: Undo).
Characteristics:
- Typically appear after a multi-select edit. eg:
- Deleting multiple photos from (Gallery)
- Deleting multiple emails (Email)
- Moving multiple emails (Email)
- Toasts are positioned at the bottom of—and layered on top of—their associated content view.
- Toasts should be non-intrusive, and never cover up other UI elements (eg: toolbar, tabs, etc).
- Optionally provide opportunity to take related secondary action via button (eg: Undo).
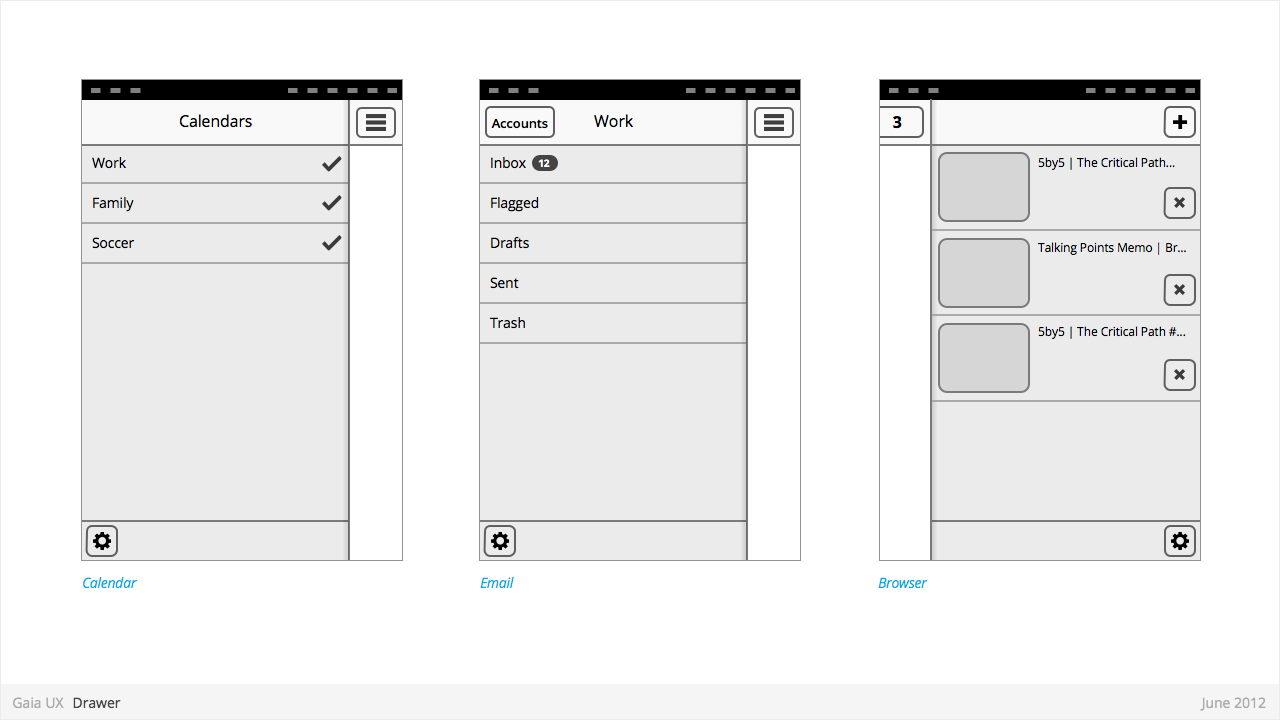
Drawer
Used for:
- Providing access to top level navigation links that may be too numerous for a Tabs pattern, or user-generated, (eg: Tabs, user accounts etc).
Characteristics:
- Provides access to top level navigation links that are usually user-configurable (eg: accounts in Email and Calendar, or tabs in Browser).
- Is also a great place to tuck secondary or power-user features, such as links to app Settings.
- Position: Should be positioned on left side of screen, but can be positioned on right in rare circumstances (eg: Browser).
- Open: should be opened via standard "Drawer" button, but other buttons can be used in rare circumstances (eg: numeric tabs button in Browser).
- Close: can be closed by tapping viewable area of the primary interface. And in future versions by swiping horizontally from bezel.
- Traditionally visually depicted as being one layer below the primary interface, and sliding in from the side via animation.
- Width: variable, but must always leave sufficient room for the "Drawer" button on the primary interface to remain fully visible.
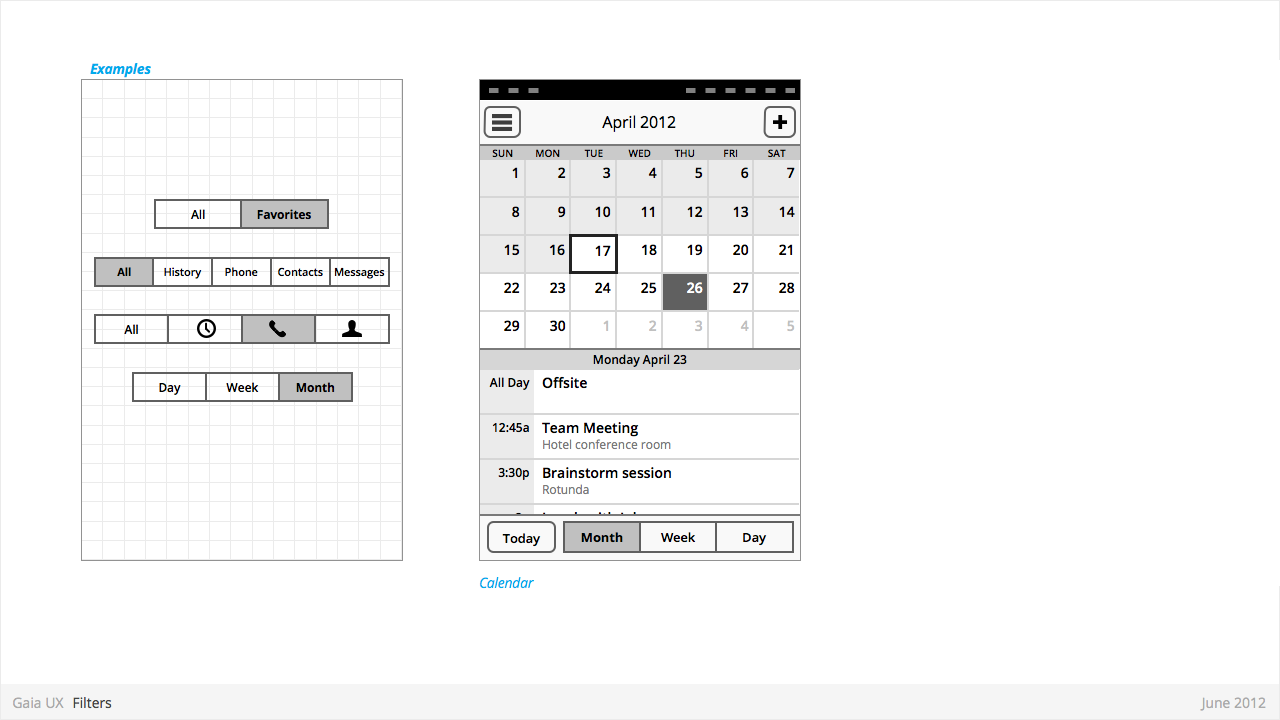
Filters
Used for:
- Secondary Navigation
- Filters can provide a second set of tabs, where tabs are already present.
- Data Filter
- Filters can be used to enable the user to view a single set of data in a different lens.
- eg: in Calendar, the filters they allow user to view time in different scales, from Day to Month).
Characteristics:
- Horizontal sequence of buttons.
- Only one button is Focused at a time.
- Best practice is to place filters within Toolbars, so they do not flow with the content.
- Left, Middle and Right buttons can be styled uniquely.
- Width: variable, depending on number of filters required within a single set (see Numbering). Should establish a maximum width, however.
- Numbering: minimum 2, maximum 5.
- Can be populated with icons or text, but not both. Because of the smaller height of a filter (versus a tab), text is the best practice.
Headers
Used for:
- Labeling the active view.
- Providing top-level navigation and inputs for the active view.
Characteristics:
- Horizontal full width bar that appears at top of screen in most apps
- Floats above content, with option to flow with content in some rare cases (eg: Browser).
- Heading text provides name of current view.
- Optional: heading text string can include text (eg: current unread email count)
- Present in most applications
Input Areas
Used for:
- ...
Characteristics:
- ...
Lists
Used for:
- ...
Characteristics:
- Varying heights (1—3 rows)
- Varying contents (from text only to image + text + button)
- Are composed of rows, and section headers
- Types:
- Action row (click anywhere to trigger input)
- Status indicator row
- Button row
- Link row
Multi-Select
Used for:
- Enables user to perform “bulk actions”, such as deleting 6 emails from a roll of 20, or selecting 3 photos to email to a friend.
- Is used on lists of items (eg: vertical list of emails in Inbox, or grid of photos in Gallery)
Characteristics:
- Is entered by...
- Is a “mode”, not a section. Animation and visual design should give user the impression that they are in a temporary mode within the original view, not that there are in a differerent view.
Can be called “Edit” or “Select” mode, depending on the use case. Header text should indicate action being taken (eg: “Select photos”). Once an item has been selected, text should update to “X selected”, where X = quantity of selected items.
- Closes once the user:
- ...completes one of the available actions (eg: “Delete”).
- ...or taps “Cancel” button.
- Closing resturns user to the previous view.
- If user has taken action (eg: delete 3 message threads), a Toast should appear, confirming the action.
States
- Normal
- Focused
- Disabled
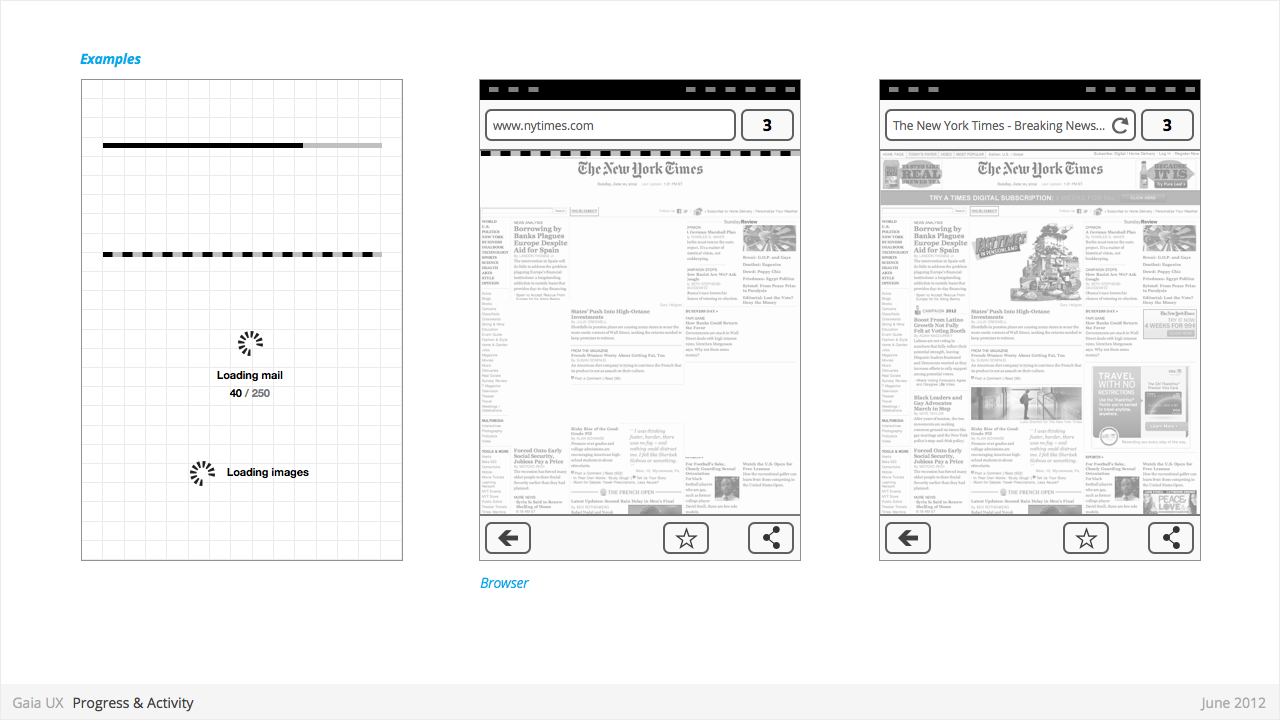
Progress & Activity Indicators
Used for:
- Providing user with visual feedback that a process is active.
Characteristics:
- May include an animated visual element, a text label, or some combination of the two.
- Types:
- Progress
- Displays a loading animation that goes from 0 to 100 percent, communicating the current process status.
- Activity
- Displays a looping animation, communicating to the user that the process is active.
- Progress
Scrolling
Used for:
- ...
Characteristics:
- Types:
- Scrollbar
- Index scrolling
Seek Bars
Used for:
- ...
Characteristics:
- Consists of track and knob (button w/ normal and pressed states)
- Optional images for left and right values
- Can be horizontal or vertical
Settings
Used for:
- ...
Characteristics:
- ...
Switches
Used for:
- ...
Characteristics:
- Presents two mutually exclusive choices or states (used in table views only).
- Types:
- On/Off toggle
- Radio
- Checkbox
Tabs
Used for:
- ...
Characteristics:
- Fill the full horizontal width.
- Number between 3—5.
- Positioned at bottom of screen.
- Can contain various elements (buttons, filters, indicators, etc).
- Versions:
- Text + icon
- Icon-only
States:
- Normal
- Focused
- Disabled
Tool Bars
Used for:
- Contains actions, indicators, and navigation associated with the current view. eg:
- Delete selected items (button)
- Refresh content (button)
- Enter “Edit” mode (filter)
- View “Favorite” contacts only (filter)
Characteristics:
- 100% width. Fixed height.
- Does not scroll with content. Floats above.
- Should be positioned at the bottom of the screen unless Tabs are also present. In that case, should be positioned at the top.
- Can contain various elements (buttons, filters, progress/activity indicators, etc).
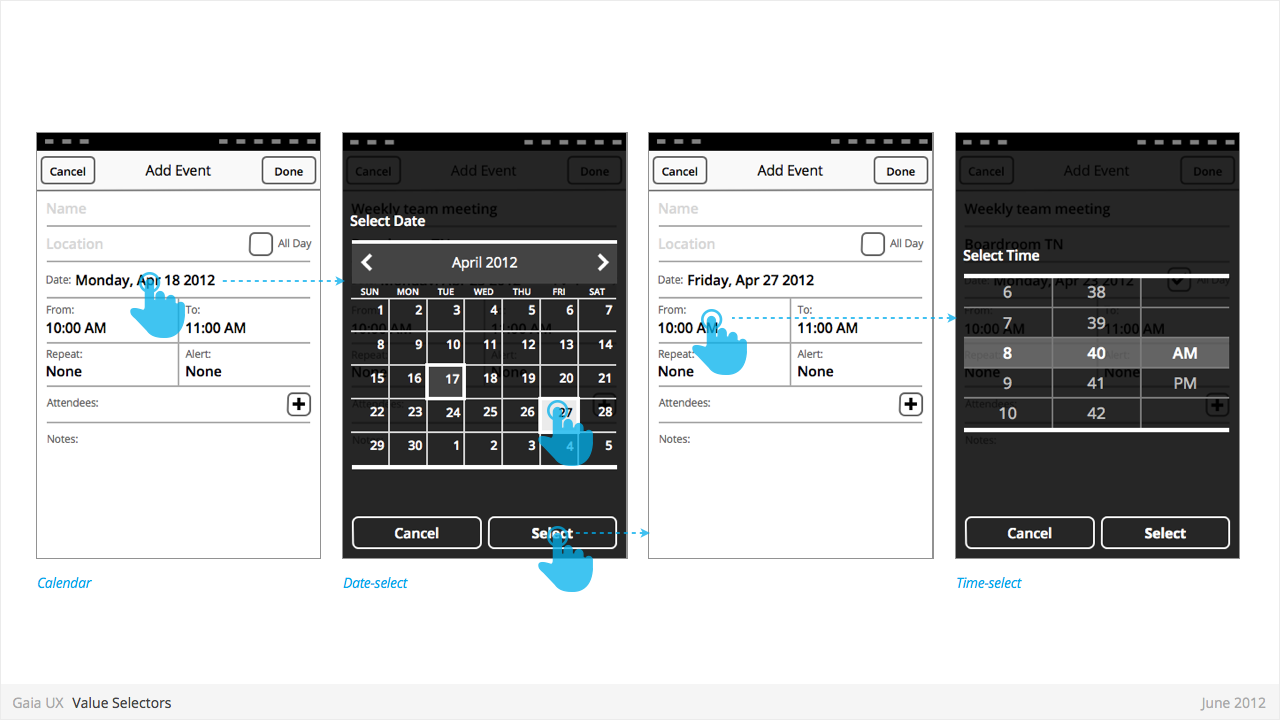
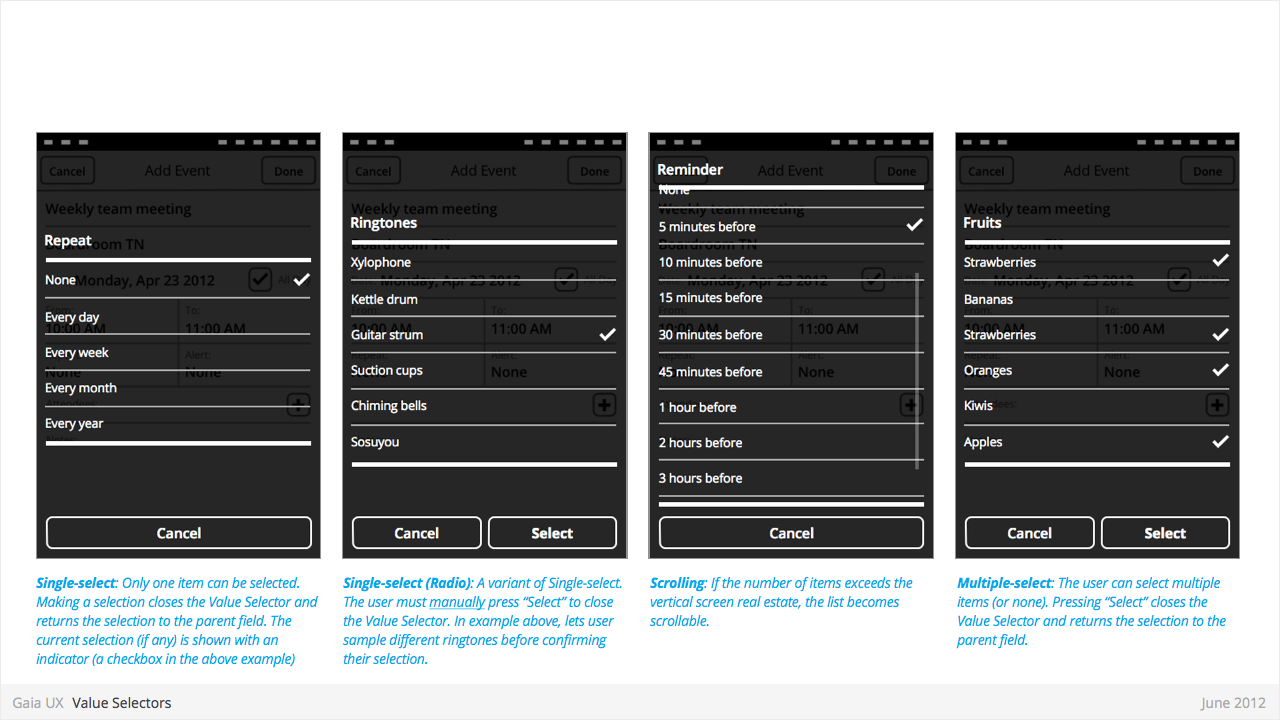
Value Selectors
Used for:
- Provides a way for the user to select one of more values.
- Most commonly associated with forms, but also used elsewhere.
- Interface conventions are flexible, and new Types can be added to the list below.
Characteristics:
- Types:
- Date
- Time
- Single-select list
- Multiple-select list