Evangelism/FontFeatures: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Supporting OpenType Font Features == | == Supporting OpenType Font Features == | ||
| Line 13: | Line 11: | ||
=== Experimental Implementation === | === Experimental Implementation === | ||
As part of this effort, Jonathan Kew has been working on porting a portion of the Pango library for use with handling complex scripts and to enable the use of font features on all supported platforms. He currently has an experimental build that uses a special CSS property to associate a list of OpenType features with specific elements in a page. This is <strong>not</strong> the [http://lists.w3.org/Archives/Public/www-style/2009Jun/0506.html proposed format], it simply provides a better way of discussing possible sets of font-variant properties and the OpenType feature settings to which they should map. | As part of this effort, Jonathan Kew has been working on porting a portion of the Pango library for use with handling complex scripts and to enable the use of font features on all supported platforms. He currently has an [http://people.mozilla.com/~jkew/feature-samples/ experimental build] that uses a special CSS property to associate a list of OpenType features with specific elements in a page. This is <strong>not</strong> the [http://lists.w3.org/Archives/Public/www-style/2009Jun/0506.html proposed format], it simply provides a better way of discussing possible sets of font-variant properties and the OpenType feature settings to which they should map. | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 27: | ||
[[File:Megalopolis.png|center|link=http://people.mozilla.com/~jkew/feature-samples/MEgalopolis.html|MEgalopolis Extra sample]] | [[File:Megalopolis.png|center|link=http://people.mozilla.com/~jkew/feature-samples/MEgalopolis.html|MEgalopolis Extra sample]] | ||
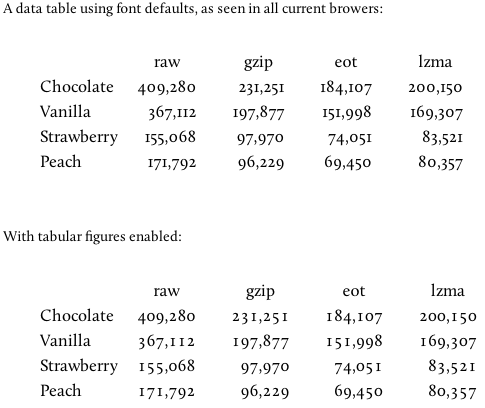
=== Tabular Figures for Numerical Alignment === | === Tabular Figures for Numerical Alignment === | ||
| Line 35: | Line 32: | ||
OpenType features also enable better control over alignment. When numbers are listed in tabular form, proportional forms often result in the misalignment of digits across rows, making the list harder to scan. With tabular alignment enabled, individual digits are rendered using a fixed width so that digits align across rows: | OpenType features also enable better control over alignment. When numbers are listed in tabular form, proportional forms often result in the misalignment of digits across rows, making the list harder to scan. With tabular alignment enabled, individual digits are rendered using a fixed width so that digits align across rows: | ||
[[File: | [[File:Flavorfigures.png|center|link=http://people.mozilla.org/~jdaggett/webfonts/tabulardata.html|Tabular Figures for Even Alignment]] | ||
=== Automatic Fractions === | === Automatic Fractions === | ||
| Line 42: | Line 39: | ||
[[File:Tiramisu.png|center|link=http://people.mozilla.org/~jdaggett/webfonts/tiramisu.html|Automatic Fractions]] | [[File:Tiramisu.png|center|link=http://people.mozilla.org/~jdaggett/webfonts/tiramisu.html|Automatic Fractions]] | ||
=== Language Sensitivity === | |||
OpenType also includes support for features on a per-language basis. This is important for rendering text correctly in some languages. For example, Turkish uses both a dotted-i and a dotless-i, so the distinction needs to be preserved when rendering ligatures or small caps. Below is the same text in English and Turkish, with both default and language-sensitive renderings shown for the Turkish text: | |||
[[File:Udhrturkish.png|center|link=http://people.mozilla.com/~jkew/feature-samples/udhr-turkish.html|Language Sensitive Rendering]] | |||
=== Historical Text === | === Historical Text === | ||
| Line 51: | Line 54: | ||
[[File:Bookexcerpt.png|center|link=http://www.bc.edu/schools/law/library/about/rarebook/exhibitions/newacq08.html|Original Scan]] | [[File:Bookexcerpt.png|center|link=http://www.bc.edu/schools/law/library/about/rarebook/exhibitions/newacq08.html|Original Scan]] | ||
Below is the same text rendered in HTML using the [http://www.iginomarini.com Fell Types revival fonts by Igino Marini] with OpenType features enabled. Note the ‘ct’ ligature and the contextual form of the ‘s’: | |||
[[File:Historicaltext.png|center|link=http://people.mozilla.org/~jdaggett/webfonts/historicaltext.html|HTML Rendering using OpenType features]] | [[File:Historicaltext.png|center|link=http://people.mozilla.org/~jdaggett/webfonts/historicaltext.html|HTML Rendering using OpenType features]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:18, 19 October 2009
Supporting OpenType Font Features
Note: the discussion below applies to work in progress, it does not describe features in Firefox 3.6.
Using @font-face allows web designers a wide palette of font choices and with commercial font vendors supporting the WOFF font format, the set of font choices should improve even more. So the next step is clearly to try and make better use of features available in these fonts.
For many years, “smart” font formats such as OpenType and AAT have provided font designers ways of including a rich set of variations in their fonts, from ligatures and swashes to small caps and tabular figures. The OpenType specification describes these features, identifying each with a unique feature tag. But these have typically only been available to those using professional publishing applications such as Adobe InDesign. Firefox currently renders using font defaults; it would be much more interesting to provide web authors with a way of controlling these font features via CSS.
Håkon Wium Lie of Opera, based on discussions with Tal Leming and Adam Twardoch, proposed extending the CSS 'font-variant' property to include values for font features. Mozilla is actively working on a new proposal along these lines. This is a fairly big addition to CSS, so it will most likely involve some complex discussions about how best to support these features.
Experimental Implementation
As part of this effort, Jonathan Kew has been working on porting a portion of the Pango library for use with handling complex scripts and to enable the use of font features on all supported platforms. He currently has an experimental build that uses a special CSS property to associate a list of OpenType features with specific elements in a page. This is not the proposed format, it simply provides a better way of discussing possible sets of font-variant properties and the OpenType feature settings to which they should map.
.altstyles {
/* format: feature-tag=[0,1] with 0 to disable, 1 to enable */
-moz-font-feature-opentype: "dlig=1,ss01=1";
}
The feature setting string above implies rendering with discretionary ligatures (dlig) and the first set of stylistic alternates (ss01). An example using Jack Usine's MEgalopolis Extra:
This font makes extensive use of OpenType features; the homepage of the font contains a sample rendering that uses many of these features. Below is a rendering of the same sample written in HTML with OpenType features enabled:
Tabular Figures for Numerical Alignment
OpenType features also enable better control over alignment. When numbers are listed in tabular form, proportional forms often result in the misalignment of digits across rows, making the list harder to scan. With tabular alignment enabled, individual digits are rendered using a fixed width so that digits align across rows:
Automatic Fractions
Automatic fractions are also possible with OpenType features, note the inline use of fractional forms in the recipe ingredient list below:
Language Sensitivity
OpenType also includes support for features on a per-language basis. This is important for rendering text correctly in some languages. For example, Turkish uses both a dotted-i and a dotless-i, so the distinction needs to be preserved when rendering ligatures or small caps. Below is the same text in English and Turkish, with both default and language-sensitive renderings shown for the Turkish text:
Historical Text
The way text is rendered constantly evolves; glyphs once in common use often morph into other forms, making the historical forms distinct from their modern forms. Below is the text of an old Massachusetts Bay Colony law, taken from a book in the Daniel R. Coquillette Rare Book Room of the Boston College Law Library.
Original scanned image:
Below is the same text rendered in HTML using the Fell Types revival fonts by Igino Marini with OpenType features enabled. Note the ‘ct’ ligature and the contextual form of the ‘s’:
Draconian laws in HTML form, what is the world coming to?